Software Tips
What is maintenance?
Maintenance refers to all measures taken to ensure the operational readiness and functionality of systems or objects. Systems can be machines, production facilities, construction elements, buildings or infrastructures, for example.
Maintenance includes not only servicing, but also other activities such as inspections, repairs, overhauls, improvements and replacements. The definition of maintenance can be found in EN 13306. EN 13306 divides maintenance into two categories: preventive maintenance and corrective maintenance.
What is meant by maintenance?
Maintenance refers to the regular checking, inspection, cleaning, adjustment and, if necessary, repair of systems to ensure their proper functioning and performance. Maintenance work is usually carried out at predetermined intervals to prevent potential breakdowns and ensure safety, extend the service life of the equipment and maximize its efficiency.
There are different types of maintenance, including preventive maintenance, which involves carrying out planned inspections and maintenance work to identify and rectify problems before they occur, and corrective maintenance, which aims to resolve problems that have already occurred.
What is meant by inspection?
An inspection in the context of maintenance refers to the systematic review of plant, machinery or equipment to assess its condition, performance and safety. During an inspection, various aspects such as wear, damage, functionality, leaks, lubrication and other relevant parameters are checked.
Inspections serve to identify potential problems at an early stage before they can lead to major failures or safety risks. They are carried out at regular intervals in accordance with a predefined inspection plan. The results of an inspection can be used to plan maintenance measures to keep the systems in optimum condition and minimize unplanned downtime.
What is meant by maintenance?
Maintenance refers to the repair or restoration to working order of plant, machinery or equipment that is defective, malfunctioning or damaged. In contrast to preventive maintenance, which is intended to prevent problems in advance, repair is a reactive measure. It is required when a problem has already occurred.
Repair can include various measures. These include the replacement of defective parts, the repair of damaged components, the readjustment of mechanisms or the restoration of functionality after a failure. The aim of maintenance is to restore the systems to an operational state as quickly as possible in order to minimize production downtime or other disruptions.
Maintenance work can be both planned and unplanned. Planned repairs can be carried out due to foreseeable wear or ageing of components, while unplanned repairs must be carried out in response to unforeseen failures or faults.
What is meant by improvement?
In the context of maintenance, improvements are measures aimed at increasing the performance, reliability, efficiency or safety of plant, machinery or equipment. In contrast to pure repair, improvement measures aim to optimize or expand existing systems.
Improvements in maintenance can take various forms, including:
- Technological upgrades
- Process optimization
Preventive measures
Training and qualification measures
What is preventive maintenance?
Preventive maintenance, also known as preventive maintenance, is a strategy for maintaining plant or machinery that aims to prevent potential failures and problems before they occur. Preventive maintenance includes, among other things:
- Regular inspections
- Maintenance work
- Parts replacement
What is corrective maintenance?
Corrective maintenance comprises activities that are carried out to rectify a failure or malfunction that has already occurred on a system or machine. This includes, among other things
- Fault detection
- Diagnosis
- Troubleshooting
- Preventive measures
Maintenance planning and control systems (IPS)
Maintenance planning and control systems (IPS) are software solutions that are used for the efficient management and control of maintenance processes in industrial companies. These systems help companies to optimize the availability, reliability and efficiency of their plant and machinery.
The main tasks of these systems include:
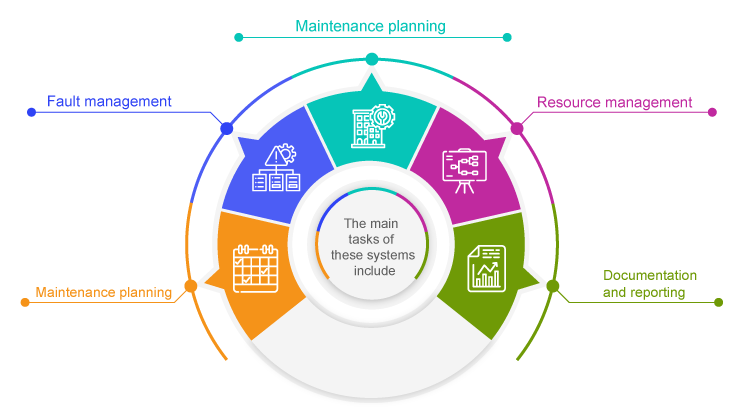
Maintenance planning
IPS helps you to plan maintenance activities for plant and machinery. You can use the system to define maintenance intervals, plan maintenance work and allocate resources such as manpower, materials and tools.
Fault management
IPS support the detection and management of faults or failures in systems. They enable a rapid response to faults by automatically sending notifications and initiating processes to rectify faults.
Maintenance planning
IPS help with the long-term planning of maintenance activities, including preventive maintenance, inspections and repairs. They take into account factors such as the service life of system components, historical maintenance data and operational requirements to create optimal maintenance plans.
Resource management
IPS enable efficient management of resources such as labor, spare parts, tools and external service providers. They help to avoid bottlenecks and ensure the availability of required resources.
Documentation and reporting
IPS usually offer features for comprehensive documentation of maintenance activities. They can usually generate reports and analyses to monitor the performance of maintenance processes, identify trends and highlight potential for improvement.
Maintenance planner or CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems)
Maintenance planners or CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) are software solutions that are used for the efficient management of maintenance processes in companies. These systems automate and simplify the planning, execution and monitoring of maintenance work on systems, machines and other equipment.
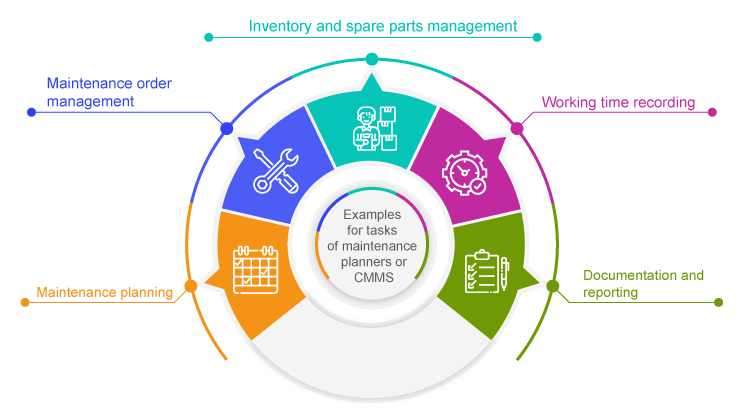
Examples of tasks for maintenance planners or CMMS
Maintenance planning
Maintenance planners support the definition of maintenance plans for various systems and equipment. They make it possible to define maintenance intervals, schedule maintenance work and allocate resources such as manpower, materials and tools.
Maintenance order management
CMMS help with the creation, assignment and tracking of maintenance orders. They record maintenance requests, prioritize orders, assign them to the appropriate employees or teams and track the progress of the work.
Inventory and spare parts management
Maintenance planners typically include functions for managing spare parts, materials and consumables required for maintenance work. They assist with inventory tracking, parts reordering and stock management to ensure that the right parts are available at the right time.
Working time recording
CMMS record labor hours and costs for maintenance activities, including hours worked, overtime and other costs. They enable accurate billing of maintenance work and monitoring of employee performance.
Documentation and reporting
Maintenance planners support the comprehensive documentation of maintenance activities, including work carried out, materials used, working times and costs. They generate reports and analyses to monitor the performance of maintenance processes, identify trends and highlight potential for improvement.
 With its convincing variety of functions, user-friendliness and low implementation effort, the modern FLUDIS software system is the suitable solution for ensuring economical, ecological and legally compliant fluid management in your company. From the planning and monitoring of your work orders to the documentation of measured values and consumption quantities as well as inventory management to the implementation of service measures such as maintenance work with mobile data acquisition directly on site, everything is possible.
With its convincing variety of functions, user-friendliness and low implementation effort, the modern FLUDIS software system is the suitable solution for ensuring economical, ecological and legally compliant fluid management in your company. From the planning and monitoring of your work orders to the documentation of measured values and consumption quantities as well as inventory management to the implementation of service measures such as maintenance work with mobile data acquisition directly on site, everything is possible. With the maintenance and servicing module, you have all maintenance and servicing work mapped in one system. Whether it's the maintenance of machines and systems, general equipment or electrical testing - you have an overview of everything. Routes or inspections, planned maintenance or repairs can be easily organized and documented.
With the maintenance and servicing module, you have all maintenance and servicing work mapped in one system. Whether it's the maintenance of machines and systems, general equipment or electrical testing - you have an overview of everything. Routes or inspections, planned maintenance or repairs can be easily organized and documented. The TOM maintenance software is a comprehensive solution (IPS, CMMS) that has been specially developed for companies that own objects of all kinds that require maintenance or that look after them on behalf of customers. This includes any technical objects from production and building technology or mobile devices. In addition to the flexible application options, the comprehensive functionality and the clear structure, which ensures simple and fast operation, are outstanding.
The TOM maintenance software is a comprehensive solution (IPS, CMMS) that has been specially developed for companies that own objects of all kinds that require maintenance or that look after them on behalf of customers. This includes any technical objects from production and building technology or mobile devices. In addition to the flexible application options, the comprehensive functionality and the clear structure, which ensures simple and fast operation, are outstanding. We have been a competent partner in the field of maintenance for industry, mountain railroads, food manufacturers and power plants for over 25 years. SAMA was developed practically in cooperation with our customers. The IPS software or the CMMS system helps you to optimize maintenance. It includes plant transparency, proof of due diligence, clear planning, revisions, spare parts availability, fault management ...
We have been a competent partner in the field of maintenance for industry, mountain railroads, food manufacturers and power plants for over 25 years. SAMA was developed practically in cooperation with our customers. The IPS software or the CMMS system helps you to optimize maintenance. It includes plant transparency, proof of due diligence, clear planning, revisions, spare parts availability, fault management ... DELECO® IMS is a maintenance management solution that maps and manages all maintenance and servicing processes for companies in industry, commerce and the municipal economy. It supports you in improving your organisation and the efficiency of the operation and maintenance process. DELECO® IMS is available either as a module of the complete ERP system DELECO® or as a stand-alone solution. Existing interfaces guarantee compatibility with other ERP systems. The multilingual and multicurrency client software ...
DELECO® IMS is a maintenance management solution that maps and manages all maintenance and servicing processes for companies in industry, commerce and the municipal economy. It supports you in improving your organisation and the efficiency of the operation and maintenance process. DELECO® IMS is available either as a module of the complete ERP system DELECO® or as a stand-alone solution. Existing interfaces guarantee compatibility with other ERP systems. The multilingual and multicurrency client software ... MaintMaster gives you full control with a range of flexible, scalable tools tailored to your business. This maintenance software (CMMS system) helps you organize, plan, unify and optimize your work. Unparalleled flexibility and optimal functionality with maximum user-friendliness.
MaintMaster gives you full control with a range of flexible, scalable tools tailored to your business. This maintenance software (CMMS system) helps you organize, plan, unify and optimize your work. Unparalleled flexibility and optimal functionality with maximum user-friendliness. GS-Service maintenance software is a powerful solution that perfectly supports you to manage your assets and equipment, create and track maintenance orders, and save costs.
GS-Service maintenance software is a powerful solution that perfectly supports you to manage your assets and equipment, create and track maintenance orders, and save costs. MOS - the software for maintenance supports companies in recording faults, assigning tasks to personnel and much more. MOS - Maintenance Organizer System maps maintenance processes relating to the systems to be maintained. You can also record when new material is required, for example, and carry out evaluations of maintenance, costs and personnel hours.
MOS - the software for maintenance supports companies in recording faults, assigning tasks to personnel and much more. MOS - Maintenance Organizer System maps maintenance processes relating to the systems to be maintained. You can also record when new material is required, for example, and carry out evaluations of maintenance, costs and personnel hours. IFS Cloud is a fully comprehensive business software for nationally and internationally active medium-sized companies. IFS Maintenance is one of the core components of IFS ERP. the functionalities include maintenance planning, linear assets, work orders, preventive maintenance, complex MRO, B2B contracting, fleet management and many more. The maintenance and repair components are part of asset management. IFS Complex MRO supports e.g. customer service by coordinating personnel, material etc..
IFS Cloud is a fully comprehensive business software for nationally and internationally active medium-sized companies. IFS Maintenance is one of the core components of IFS ERP. the functionalities include maintenance planning, linear assets, work orders, preventive maintenance, complex MRO, B2B contracting, fleet management and many more. The maintenance and repair components are part of asset management. IFS Complex MRO supports e.g. customer service by coordinating personnel, material etc.. CMMS - Maintenance planning and control system (IPS)
Maintenance planning and control is one of the most important aspects of asset management for many organisations...
CMMS - Maintenance planning and control system (IPS)
Maintenance planning and control is one of the most important aspects of asset management for many organisations... RAMS-Office NG supports you in your system environment in your day-to-day business with a flexible workflow. The software is the basic tool for recording RAMS/LCC-relevant data. The software offers functions for standardizable or customizable report generation and graphical results processing.
RAMS-Office NG supports you in your system environment in your day-to-day business with a flexible workflow. The software is the basic tool for recording RAMS/LCC-relevant data. The software offers functions for standardizable or customizable report generation and graphical results processing. Increase safety in your company with the cloud-based PPE audit software. With PPE-Audit, you always have an overview of your PPE(gA) and are always informed when an item is due for inspection or has reached the end of its product life cycle. Manage your PPE items conveniently and in compliance with the law!...
Increase safety in your company with the cloud-based PPE audit software. With PPE-Audit, you always have an overview of your PPE(gA) and are always informed when an item is due for inspection or has reached the end of its product life cycle. Manage your PPE items conveniently and in compliance with the law!... The MODUS ERP solution is particularly designed for all production processes in plastics and metal processing. Functions are available for precise forecasting and planning, predictive maintenance and much more. MODUS INDUSTRY covers all production process steps and integrates the necessary data based on MS Dynamics.
The MODUS ERP solution is particularly designed for all production processes in plastics and metal processing. Functions are available for precise forecasting and planning, predictive maintenance and much more. MODUS INDUSTRY covers all production process steps and integrates the necessary data based on MS Dynamics. luxData is a management information system that has been used successfully in the lighting industry for many years. It covers all requirements in the management of general street lighting and commercial outdoor lighting. The software maps all relevant street lighting data and energy data and simplifies fault recording, maintenance, servicing, DMS, evaluations and reporting. Additional modules and interfaces allow luxDat to be adapted even more specifically to your needs.
luxData is a management information system that has been used successfully in the lighting industry for many years. It covers all requirements in the management of general street lighting and commercial outdoor lighting. The software maps all relevant street lighting data and energy data and simplifies fault recording, maintenance, servicing, DMS, evaluations and reporting. Additional modules and interfaces allow luxDat to be adapted even more specifically to your needs. CONVAL is a calculation and optimization program for instrumentation, piping and process engineering. It offers easy operation, extensive functions and high accuracy. CONVAL is the ideal tool for maintenance and planning engineers.
CONVAL is a calculation and optimization program for instrumentation, piping and process engineering. It offers easy operation, extensive functions and high accuracy. CONVAL is the ideal tool for maintenance and planning engineers.