Software Tips
What is an inventory management system?
An inventory management system, also called merchandise management, is a software for tracking the inventory and all goods movements in a company. It includes all processes in purchasing and sales, warehousing and shipping. All goods that a company purchases or even produces are recorded in the inventory management system. The underlying data of an inventory management system thus consists of the master data for articles, suppliers and customers as well as the transaction data for offers, orders, delivery bills, notifications and invoices.
Interfaces can connect the inventory management system to cash register systems, online stores or invoicing programs. Since inventory management systems are usually modular, there are often additional modules for CRM, returns or device management, for example.
Differences between inventory management systems
The difference between inventory management and ERP
Since most inventory management systems are modular, the boundary to ERP is rather blurred. An ERP maps the entire value chain of a company. This also includes personnel, marketing and, for example, controlling. These modules or functions are not normally integrated in an inventory management system. However, this is the case the other way around, because inventory management systems are usually part of an ERP system.
An inventory management system is therefore either a stand-alone system with interfaces to other third-party systems or part of a comprehensive ERP system. Central systems, as the name suggests, are assigned to the company headquarters. Decentralized inventory management are the ones that are connected to the corporate headquarters. In connection with inventory management systems, we also often speak of closed, open or integrated inventory management systems.
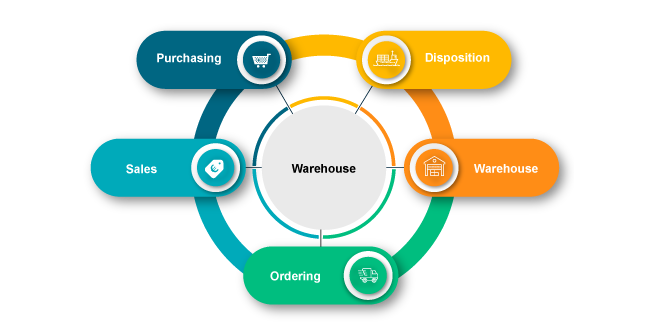
Closed inventory management system
One speaks of a closed inventory management system when purchasing and sales, ordering, disposition and warehouse are mapped within one system. This can be data on the individual goods, the suppliers, quantity, value, date of receipt, etc.. Often the data acquisition at the receipt as well as at the storage and transfer as well as at the dispatch is done by barcode scanners and the use of EAN codes.
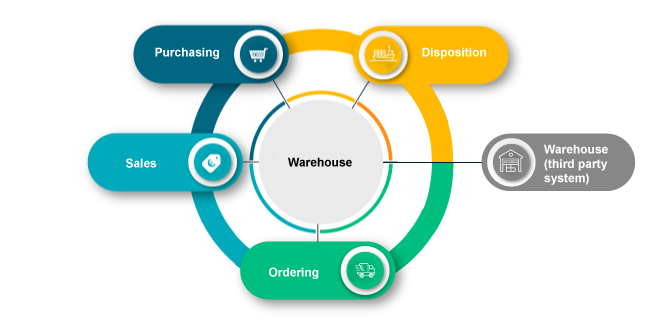
Open inventory management system
An open inventory management system is made up of individual modules, in which one module is taken over from a third-party system. The open enterprise resource planning system also includes goods receipt and goods issue. Depending on the provider, it can also map materials planning, purchasing, ordering and warehouse management. In an open inventory management system, however, the individual modules do not all have to come from the same system. In an open system, goods receipts and goods issues are recorded in the master software in any case.
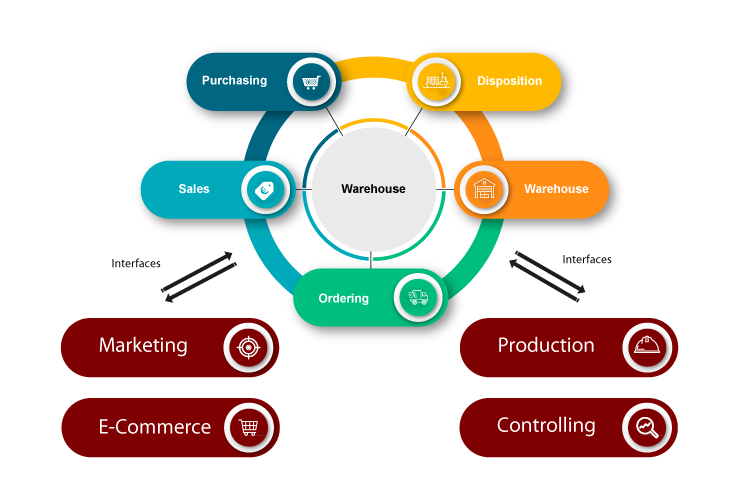
Integrated inventory management system
Integrated inventory management systems usually include all the necessary modules that a closed system also has. They also offer interfaces to third-party systems so that store systems, marketplaces, suppliers or banks can be integrated, for example. Integration is differentiated between internal and external integration. An internal integration is, for example, the connection of the head office software with the inventory management of the individual stores. In external integration, the company's own inventory management system is linked to the merchandise management systems of various partners within the supply chain.
In which companies is an inventory management system used?
All companies that keep goods in a warehouse need an inventory management system. Inventory management systems are therefore used in particular in trading and logistics companies. Trading companies purchase goods and resell these goods. This applies to both retailers and wholesalers and is independent of whether trading is done exclusively online or also with a retail store. The vast majority of trading companies are not simultaneously the producers of the goods they handle. However, it is quite common to refine purchased goods, to put together bundles or kits.
Inventory management systems can be designed to be industry-neutral or geared to the requirements of specific industries such as food retailing or pharmaceutical retailing, for example. Many of the inventory management systems support online retailing or are able to map several sales channels at the same time (multichannel solutions).A central merchandise management system that is linked to a wide variety of channels such as eBay, Amazon, other online stores, etc. can efficiently output data to the various online sales platforms via interfaces.
 Die webbasierte twoeyes enterprise Warenwirtschaft eröffnet Ihnen eine Vielzahl an neuer Chancen und Möglichkeiten. Managen Sie sämtliche Waren und Artikel auf Basis präziser Stammdaten und mit einem äußerst professionellen Auftrags-, Lager- und Versandwesen. Optimieren Sie Ihre Produktion nach Kanban und/oder individuellen QM-Vorgaben. Definieren Sie Ihre Preise, Preisgruppen und Staffelpreise, planen Sie Sonderverkaufsaktionen und verknüpfen Sie die Wawi mit Ihrem Online-Shop.
Die webbasierte twoeyes enterprise Warenwirtschaft eröffnet Ihnen eine Vielzahl an neuer Chancen und Möglichkeiten. Managen Sie sämtliche Waren und Artikel auf Basis präziser Stammdaten und mit einem äußerst professionellen Auftrags-, Lager- und Versandwesen. Optimieren Sie Ihre Produktion nach Kanban und/oder individuellen QM-Vorgaben. Definieren Sie Ihre Preise, Preisgruppen und Staffelpreise, planen Sie Sonderverkaufsaktionen und verknüpfen Sie die Wawi mit Ihrem Online-Shop. Merchandise management can be so simple - with Bison Process Retail (x-trade) With Bison Process Retail (x-trade), merchandise management can be so uncomplicated for retailers. As a complete solution, this software offers numerous advantages that can be applied at all levels of retail. From wholesale to retail with or without stores, you benefit from the various modules that can be optionally added as supplements for the basic version. Ultimately, your entire retail chain can be mapped and processed centrally ...
Merchandise management can be so simple - with Bison Process Retail (x-trade) With Bison Process Retail (x-trade), merchandise management can be so uncomplicated for retailers. As a complete solution, this software offers numerous advantages that can be applied at all levels of retail. From wholesale to retail with or without stores, you benefit from the various modules that can be optionally added as supplements for the basic version. Ultimately, your entire retail chain can be mapped and processed centrally ... deLUXE-ERP is an intelligent ERP solution for small and medium-sized companies. The standard version of the system already includes all the functionalities required to map the most important business processes such as acquisition, sales, distribution and finance in a single, integrated application. A sophisticated reservation system in order processing ensures on-time deliveries. You can efficiently create quotations, generate orders, organise deliveries and keep the warehouse up to date.
deLUXE-ERP is an intelligent ERP solution for small and medium-sized companies. The standard version of the system already includes all the functionalities required to map the most important business processes such as acquisition, sales, distribution and finance in a single, integrated application. A sophisticated reservation system in order processing ensures on-time deliveries. You can efficiently create quotations, generate orders, organise deliveries and keep the warehouse up to date. In addition to numerous basic functions, Wema's reliable merchandise management system also offers useful value-added functions, such as the management of several companies and rights and user administration including password protection.
In addition to numerous basic functions, Wema's reliable merchandise management system also offers useful value-added functions, such as the management of several companies and rights and user administration including password protection. TaxMetall is a modular ERP system / PPS system with document management for digitization and a production module for manufacturing. The business solution is for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the areas of contract, series and contract manufacturing as well as CNC processing and machining. Production data acquisition, personnel time recording and mobile apps can be integrated, as can CAD.
TaxMetall is a modular ERP system / PPS system with document management for digitization and a production module for manufacturing. The business solution is for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the areas of contract, series and contract manufacturing as well as CNC processing and machining. Production data acquisition, personnel time recording and mobile apps can be integrated, as can CAD. The merchandise management system allows you to manage and track millions of items. Whether it's stock transfers, price changes or repeat orders, the merchandise management system automatically makes suggestions. With the dashboard, you can keep an eye on all company data and receive analyses in real time. The particular strengths of our retail software lie in fashion, sports and lifestyle retail.
The merchandise management system allows you to manage and track millions of items. Whether it's stock transfers, price changes or repeat orders, the merchandise management system automatically makes suggestions. With the dashboard, you can keep an eye on all company data and receive analyses in real time. The particular strengths of our retail software lie in fashion, sports and lifestyle retail. vcEuroFaktura includes all the functionalities that self-employed entrepreneurs, freelancers or craftsmen expect from an order processing software and that with a high level of usability. For more than 15 years, the software has been specially optimised for the requirements of invoicing from Germany. The structure of the software is divided into logical processes and is clearly structured.
vcEuroFaktura includes all the functionalities that self-employed entrepreneurs, freelancers or craftsmen expect from an order processing software and that with a high level of usability. For more than 15 years, the software has been specially optimised for the requirements of invoicing from Germany. The structure of the software is divided into logical processes and is clearly structured. VENTAS is a contemporary software and organisation solution for companies in national and international trade. The VENTAS series is based on a modular architecture. Our solution is based on a selection of approx. 1,000 components (parameterisable individual programmes), which form an optimised solution for an area. VENTAS.import, for example, represents an optimised solution for import. For this purpose, we have developed a utilisation concept for the software that covers all important concerns ...
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)...
VENTAS is a contemporary software and organisation solution for companies in national and international trade. The VENTAS series is based on a modular architecture. Our solution is based on a selection of approx. 1,000 components (parameterisable individual programmes), which form an optimised solution for an area. VENTAS.import, for example, represents an optimised solution for import. For this purpose, we have developed a utilisation concept for the software that covers all important concerns ...
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)... IX FUSION PLUS is a complete merchandise management system from the entry and management of master data, order entry, procurement, goods receipt (warehouse, materials management), allocation and invoicing. State-of-the-art database technology enables you to enter data flexibly and without limits. The system is multi-client capable and runs Windows-based. This allows for quick familiarisation and low follow-up costs. It includes integrated standard reports that can be customised on request.
IX FUSION PLUS is a complete merchandise management system from the entry and management of master data, order entry, procurement, goods receipt (warehouse, materials management), allocation and invoicing. State-of-the-art database technology enables you to enter data flexibly and without limits. The system is multi-client capable and runs Windows-based. This allows for quick familiarisation and low follow-up costs. It includes integrated standard reports that can be customised on request. IX FUSION LITE is the comprehensive and powerful business software for the fashion, textile and clothing industry. The ERP software impresses with its user-friendly, fresh and modern interface. Best practice, customized application scenarios, comprehensive analysis tools, KPI considerations, use of data warehouses, business logic and a multi-tier approach are just some of the highlights.
IX FUSION LITE is the comprehensive and powerful business software for the fashion, textile and clothing industry. The ERP software impresses with its user-friendly, fresh and modern interface. Best practice, customized application scenarios, comprehensive analysis tools, KPI considerations, use of data warehouses, business logic and a multi-tier approach are just some of the highlights. ERP industry solution for meat - Well-founded industry know-how combined with the use of the latest software technology forms the basis for the success of the specialised ERP industry solution. From procurement, slaughtering and cutting through production and recipe optimisation to integrated price labelling and efficient order picking ...
ERP industry solution for meat - Well-founded industry know-how combined with the use of the latest software technology forms the basis for the success of the specialised ERP industry solution. From procurement, slaughtering and cutting through production and recipe optimisation to integrated price labelling and efficient order picking ... The SRM adaptive ERP controller continuously calculates and updates order-relevant MRP parameters for all your items. These parameters include reorder point, material safety requirement, safety stock, replenishment times in procurement, dead and idle times between operations, and theoretical machine capacity. SRM automatically compares the data from the ERP system with the company's target key figures and changes the corresponding parameters in case of deviations.
The SRM adaptive ERP controller continuously calculates and updates order-relevant MRP parameters for all your items. These parameters include reorder point, material safety requirement, safety stock, replenishment times in procurement, dead and idle times between operations, and theoretical machine capacity. SRM automatically compares the data from the ERP system with the company's target key figures and changes the corresponding parameters in case of deviations. The modular, scalable ERP software Odoo can be perfectly adapted to your exact operational requirements. We offer an ERP and the associated digitisation of your company from a single source, so that your digitisation process runs smoothly and error-free. Instead of individual software modules for sub-areas of your company, you get a system from a single source as required.
The modular, scalable ERP software Odoo can be perfectly adapted to your exact operational requirements. We offer an ERP and the associated digitisation of your company from a single source, so that your digitisation process runs smoothly and error-free. Instead of individual software modules for sub-areas of your company, you get a system from a single source as required. With the brixxbox, GEBRA-IT has created a somewhat different merchandise management solution. Using a variety of ready-made building blocks, your company's merchandise management and administration can be quickly and individually mapped by combining these building blocks. GEBRA-IT consistently pursues the goal of consistently supporting and integrating all economic processes and workflows with efficient merchandise management functionalities.
With the brixxbox, GEBRA-IT has created a somewhat different merchandise management solution. Using a variety of ready-made building blocks, your company's merchandise management and administration can be quickly and individually mapped by combining these building blocks. GEBRA-IT consistently pursues the goal of consistently supporting and integrating all economic processes and workflows with efficient merchandise management functionalities. Solution2 offers fully integrated merchandise management software that optimizes purchasing, sales and warehouse processes. Thanks to the central database, duplicate data entry is a thing of the past and you increase efficiency in all areas of merchandise management.
Solution2 offers fully integrated merchandise management software that optimizes purchasing, sales and warehouse processes. Thanks to the central database, duplicate data entry is a thing of the past and you increase efficiency in all areas of merchandise management. The TOPIX business software comprehensively maps all organizational and administrative functions in one program – and it does so in a user-friendly way and with a clear user interface. The software can be used on both Windows and Mac, as well as in mixed environments. All basic functions can be used across different industries. The range of functions includes, among other things, multiple vendor management, quotation management, calculation, procurement, workflow, multi-warehouse capability, and much more. The software is multilingual and multi-client capable.
The TOPIX business software comprehensively maps all organizational and administrative functions in one program – and it does so in a user-friendly way and with a clear user interface. The software can be used on both Windows and Mac, as well as in mixed environments. All basic functions can be used across different industries. The range of functions includes, among other things, multiple vendor management, quotation management, calculation, procurement, workflow, multi-warehouse capability, and much more. The software is multilingual and multi-client capable.